How is RTSP usage supported with Bosch VIP Devices?
Question
How is RTSP usage supported with Bosch VIP Devices?
Answer
1 Intro
The Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) allows live viewing of video and replay of recorded video from a BVIP encoder or IP camera with a compatible standard media player. VRM also supports RTSP, so it is possible to view live view or replay of a phisical camera over VRM
Note
There is a document that describes the RTSP support for Bosch VIP devices .
»Standard« in this way has the meaning of »implemented according to the RTSP standard« RFC 2326. RTSP support has been added to MPEG4 SH++ BVIP encoders and IP cameras with firmware 3.0. H.264 RTSP streaming is supported since firmware version 4.0 and with firmware version 4.10 audio support has been included. In addition, firmware version 4.10 provides ONVIF compliance (and JPEG streaming).
The Video LAN Client (VLC) or any other RTSP compatible player can be used as a test client for the RTSP connection,
independent of the used platform (Windows, Macintosh, Linux, ...).
Note
Please note that the RTP payload type which is used for H.264 video is fixed to the value 35. While parsing the RTP session H.264 video is only to be expected in this payload type.
The encoding profiles within the encoder must be set up properly to allow connections via RTSP. All supported resolutions and encoding profiles are available through RTSP.
The URL for the requested video stream may look like:
RTSP://160.10.0.1/<<parameter_string>>
Note
There is additional document that describes the RTSP support for VRM.
_______________________________________________________________
The following examples assume
Dinion IP camera installed at the IP address 160.10.0.1
VideoJet X40 XF E installed at the IP address 160.10.0.40 with 4 cameras connected
The <<parameter_string>> syntax and valid parameters are described in section 3 Available RTSP Parameters, page 4; however one may already get a feeling for the syntax in the next chapter.
2 Examples
2.1 Setting up a live connection
Connecting to a BVIP unit is as simple as entering a URL that specifies the protocol and the unit’s IP address. An RTSP connection from e.g. VLC to the Dinion IP is established
by opening the File menu, choosing Open network and entering:
RTSP://160.10.0.1
This will show live video from the Dinion IP camera, using encoding stream 1. Reception of stream 2 is accomplished by handing over the parameter inst to the Dinion IP's RTSP server.
The RTSP server inside the Bosch IP Video unit doesn't need a web page addressed in the URL but needs the slash after the IP address followed by the question mark as a separator for the query string that carries the parameter(s). Therefore the request should look like:
RTSP://160.10.0.1/?inst=2
2.2 Setting up a replay connection
Note
Replay of recorded video via RTSP works for locally managed recordings or centrally managed (VRM) recordings, but require VRM version 3.0 or higher and firmware version 5.70 or higher.
To establish a replay connection over RTSP the URL needs some additional parameters. The connection is set-up with the following URL:
RTSP://160.10.0.1/rtsp_tunnel?rec=1&rnd=718
This will show the recorded video of stream 1. The recording is replayed by default with normal speed (100 %) and the starting point of the session is the start time of the last recorded slice. The random number (rnd) in the URL is necessary to enable further actions with the recorded stream, like replay from a specific time, or search for recordings by means of RCP+. The parameter is to be interpreted as a bool value and does not reference a specific recording (for further information see section Recorded video stream selection).
NTP time mapping of the conveyed RTP timestamps is explained in section 4.4 RTP replay timestamp, NTP time mapping.
2.3 Selecting a camera from a multichannel unit
Similar to the example above, an RTSP connection from VLC to the VideoJet X40 XF E is established by opening the File menu, choosing Open network and entering:
RTSP://160.10.0.40
This would show live video from the first camera on the VideoJet X40 XF E, using stream 1. The video inputs and the respective cameras are selectable through the line parameter. To connect to the video feed from the second
camera, the URL needs look like:
RTSP://160.10.0.40/?line=2
Multiple parameters can be handed over equal to standard query string notation in an URL, separated by &.The order of the parameters in the query string is not relevant.
An RTSP connection to the second encoding stream of camera 3 would require the following URL:
RTSP://160.10.0.40/?line=3&inst=2
_______________________________________________________________
2.4 Setting up a Multicast connection
Given a scenario where multiple users need to connect to one live source one multicast session is preferable to multiple unicast streams. Multicast RTSP connections are established using the multicast parameter. The resulting
URL to join the multicast RTSP stream from the Dinion IP would be:
RTSP://160.10.0.1/?multicast=1
Similarly, joining a multicast RTSP stream from the fourth camera and the second encoding stream of the VideoJet X40 XF E is accomplished by entering the URL:
RTSP://160.10.0.40/?line=4&inst=2&multicast=1
2.5 Selecting the stream encoding type
Since firmware version 4.0 Bosch IP Video units allow the selection of the encoding type for the streamed video (depending on the device's encoding capabilities) with the h26x parameter.
The supported encoding types are:
JPEG h26x=0
MPEG-4 SH++ h26x=3
H.264 h26x=4
H.265 h26x=5
Note
The parameter h26x is not recognized by VRM and h26x can be omitted when VRM stream is requested. If encoded in H264 then the delivered stream is H264, if encoded with H265, then H265 stream is delivered.
There is additional document that describes the RTSP support for VRM.
Thus, explicitly specifying the stream encoding for an MPEG-4 SH++ stream would require the following URL:
RTSP://160.10.0.1/?h26x=3
Accordingly, a H.264 streaming request looks like:
RTSP://160.10.0.1/?h26x=4
Alternatively, JPEG streaming is requested with the following URL:
RTSP://160.10.0.1/?h26x=0
2.6 Setting up a video connection with audio
Some Bosch IP Video units are equipped with audio inputs.
As an example, a VideoJet X40 XF E provides two audio inputs. Enabling an audio connection along with the video stream requires different parameters to be used (see example below).
The first parameter (enableaudio) enables audio in general and needs to be set to 1. The second parameter (audio_line) identifies the audio input that is streamed in conjunction with the video. This parameter and its values are used similarly to the line parameter.
For an RTSP connection that would show live video from the first camera on the VideoJet X40 XF E together with audio from the first audio input, the URL must look like:
RTSP://160.10.0.40/?line=1&enableaudio=1&audio_line=1
Audio and video inputs are usually used together. Thus, addressing only the audio input without the video line parameter will automatically connect the corresponding video input. The following URL establishes the same video
and audio connections as the previous example:
RTSP://160.10.0.40/?enableaudio=1&audio_line=1
_______________________________________________________________
If a certain audio input shall be attached to a certain video input the parameters must be given accordingly. To conjoin the second audio input with the fourth video input the URL looks like:
RTSP://160.10.0.40/?line=4&enableaudio=1&audio_line=1
Note
Please note that in this case the line parameter must be provided in advance of the audio_line parameter. Otherwise the conjoin default mechanism would step in and the additional line parameter would be discarded.
For a Multicast RTSP connection with H.264 streaming from our VideoJet X40 XF E’s camera 3, using the second stream, while listening to the signal from the first audio input, the URL must look like:
RTSP://160.10.0.40/?h26x=4&line=3&inst=2&multicast=1
&enableaudio=1&audio_line=1
3 Available RTSP Parameters
3.1 General
RTSP parameters can be handed over the BVIP RTSP server by means of a URI query string as defined in RFC 3986 (http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.4).)
3.2 Setup parameters
3.2.1 Live video stream selection
This parameter selects the video instance (video stream) to be retrieved through RTSP.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | inst |
Values | 1 = stream1 |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?inst=2 |
3.2.2 Enable replay mode
This parameter enables the device's replay mode, which means that a recorded video stream is being streamed through RTSP.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | rec |
Values | 0 or 1 (as bool; enabled or disabled; |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?rec=1 |
_______________________________________________________________
3.2.3 Recorded video stream selection
This parameter selects the recorded video stream that is to be replayed. This selection always goes along with the rec parameter.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | inst |
Values | 1 = recording1 |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?inst=2&rec=1 |
3.2.4 Replay speed
With FW 5.90 an additional RTSP parameter for controlling the speed of a replay session has been added.
The speed is controlled in percent, where a value of 100 represents ‘realtime’. Negative values represent a replay in reversed direction. This is a best effort approach and once the device is not able to catch up with a set replay speed the packets are sent out as fast as possible.
Values above 1000000 are interpreted as iFrame only mode, which allows for speed manipulation through the addition of the replay speed percentage to this value.
That means that a value of 1000100 requests an iFrame only stream in realtime, whereas a value of 1001000 requests an iFrame only stream in 1000% of the realtime speed (10 x realtime).
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | speed |
Values | -2000 … 2000 (replay speed as percentage of realtime; negative values trigger playback in reverse direction; 100 represents realtime) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?rec=1&speed=200 RTSP://160.10.0.1/?rec=1&speed=1003000 |
3.2.5 Seek parameter
With FW 5.90 an additional RTSP parameter for seeking to a certain point in time of a recording has been added.
The seek time is given in ‘local time’ of the device and is calculated in seconds since Jan. 1st 2000, midnight.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | seek |
Values | number (seconds since Jan. 1st |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?rec=1&seek=0x0 |
3.2.6 Random number
This parameter defines a random number which is needed to retrieve the RTSP session ID with the help of RCP+.
This parameter usually goes along with the rec parameter.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | rnd |
Values | random number |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?rnd=718&rec=1 |
3.2.7 Replay session setup
This parameter adds a generic FMTP line to the session description during the session setup for a replay stream.
By default, the SDP in the session setup does not contain an FMTP line as all the necessary parameters are transmitted in-line with the first replay packets. Some clients need this information during setup, though. (General availability FW 6.40 and above)
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | fmtp |
Values | 0 or 1 (as bool; false or true) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?fmtp=1 |
_______________________________________________________________
3.2.8 Establish RTSP tunnel
This parameter enables a tunneled (port 80) TCP media connection.
Setting up VLC for TCP tunneling needs adjustments of VLC's advanced options (see Setting up VLC for RTP/TCP tunneling)
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | rtsp_tunnel |
Values | |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/rtsp_tunnel |
Note
Please note that the rtsp_tunnel parameter is not part of the query string! Furthermore, the parameter does not change the media transport mode. The media session setup (transport mode) is specified
during connection setup (in the RTSP SETUP request). A brief overview of the various RTSP transport modes can be found in section RTSP/RTP setup modes.
3.2.9 Video line selection
This parameter selects the video line (for multi input devices) to be retrieved through RTSP. Since VRM version 3.10 this parameter can also be used to address a track list entry of the VRM.
Note
There is additional document that describes the RTSP support for VRM.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | line |
Values | selects the corresponding line or the |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?line=1 |
3.2.10 Enable video
This parameter enables or disables video in the RTP session. Video is enabled by default.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | enablevideo |
Values | 0 or 1 |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?enablevideo=0 |
3.2.11 Enable video authentication
This parameter enables and disables video authentication. The authentication itself needs to be configured via Bosch RCP+ protocol.
(General availability FW 6.32 and above)
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | auth |
Values | 0 = no video authentication |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?auth=1 |
_______________________________________________________________
3.2.12 Enable audio
This parameter enables or disables audio in the RTP session.
Audio is disabled by default. By enabling audio without specifying the audio_mode parameter, the G.711 audio encoding type is used as default.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | enableaudio |
Values | 0 or 1 |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?enableaudio=1 |
3.2.13 Select the video encoding type
This parameter selects the video encoding type for the RTP session.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | h26x |
Values | 0 = JPEG |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?h26x=0 |
3.2.14 Select the audio encoding type
This parameter selects the audio encoding type for the RTP session.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | audio_mode |
Values | 0 = AAC |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?audio_mode=0 |
3.2.15 Enable ONVIF metadata
This parameter enables or disables ONVIF IVA events. If no metaline is specified, video line 1 is taken as default.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | meta |
Values | 0 or 1 (as bool; false or true) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?meta=1 |
3.2.16 Disable ONVIF replay header extension
This parameter enables or disables the addition of the ONVIF replay header extension for RTSP replay sessions (see also section RTP replay timestamp, NTP time mapping)
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | onvifhdr |
Values | 0 or 1 (as bool; false or true) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?rec=1&onvifhdr=0 |
3.2.17 Select line for ONVIF metadata
This parameter selects the input line for the creation of ONVIF IVA events.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | metaline |
Values | number (input line for the creation of |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?metaline=1 |
3.2.18 Enable Bosch VCA data
This parameter enables or disables the transmission of Bosch VCA data.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | vcd |
Values | 0 or 1 (as bool; false or true) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?vcd=1 |
_______________________________________________________________
3.3 Multicast parameters
3.3.1 Preliminary note
The configured multicast settings on a device's web page used to be independent from the RTSP multicast settings, since the RTSP stack merely just acted as a RTP relay on the device and did not synchronize with the RCP+
connections or settings.
Practically this lead to some issues in networks where RCP+ and RTSP multicast streams were pulled and hence a synchronization mechanism between the web page settings of the device and the RTSP multicast group
was introduced. That means that the device is using the configured multicast group and port for video.
The adjacent audio port is the video port + 2.
A JPEG session will use the settings for video stream 1 and the port is the video port + 8.
This synchronization was introduced with FW 5.90 (5.72 for CPP3 devices) and is available from thereon.
3.3.2 Enable multicast
This parameter enables multicast streaming on the Bosch VIP devices.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | multicast |
Values | 0 or 1 (as bool; false or true) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?multicast=1 |
3.3.3 Video port
This parameter sets the port, which is used for the multicast video session.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | mc_port_video |
Values | number (selects video multicast port) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/ |
3.3.4 Video IP address
This parameter sets the IP address, which is used for the multicast video session.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | mc_group_video |
Values | IP address string (selects video multicast address) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/ |
3.3.5 Audio port
This parameter sets the port, which is used for the multicast audio session.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | mc_port_audio |
Values | number (selects audio multicast port) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/ |
_______________________________________________________________
3.3.6 Audio IP address
This parameter sets the IP address, which is used for the multicast audio session.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | mc_group_audio |
Values | IP address string (selects audio multicast address) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/ |
3.3.7 Metadata port
This parameter sets the port, which is used for the multicast metadata session.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | mc_port_meta |
Values | number (selects metadata multicast |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/ |
3.3.8 Metadata IP address
This parameter sets the IP address, which is used for the multicast metadata session.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | mc_group_meta |
Values | IP address string (selects metadata |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/ |
3.3.9 Retriggering the multicast connection
RTSP multicast connections need a retrigger event to keep the connection alive. This behavior can be disabled by setting mcRetrigger=0 in the RTSP URL for environments where no keep-alive messages are sent. Otherwise the connection times out after 1 minute.
Any RTSP request can be used as a keep-alive. Usually an OPTIONS or GET_PARAMETER request is a good choice for a keep-alive message. Also an RTCP ReceiverReport is interpreted as a keep-alive packet; RTCP RRs are only
available in unicast sessions, though.
If the device is set to 'not expect retrigger packets' a connection needs to be shut down explicitly with an RTSP TEARDOWN request.
If such a request is not sent, the connection is kept open 'forever'. For this reason the mcRetrigger parameter should only be used when its intention is clear and no other way of retriggering the connection is available.
With FW 5.90 and FW 5.73 the retrigger issued with VLCbased implementations are solved inside the devices' RTSP server and this parameter should be considered as obsolete.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | mcRetrigger |
Values | 0 or 1 (as bool; false or true) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/ |
3.4 Transcoder parameters
Since FW 5.90 some RTSP parameters to control the transcoder functionality have been added to the transcoder interface and in addition also an RTSP input
interface was added. Such an interface allows the transcoder to act as an RTSP client and basically transcode any RTSP/RTP H.264 video source.
The following picture displays the general building blocks of such a scenario.
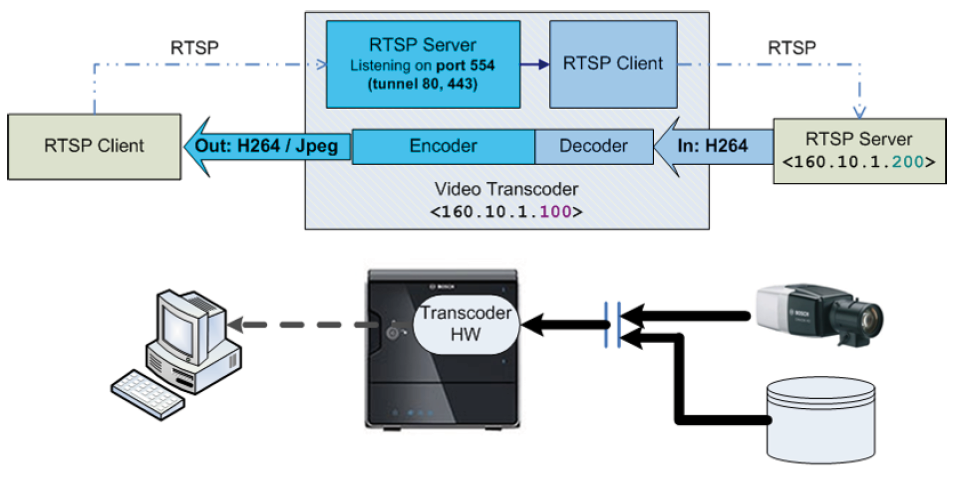
Available transcoder parameters are as follows:
3.4.1 Enable the transcoder
This parameter enables the transcoder (e.g. in case a transcoder instance of a Video Jet X20/X40 XFE) is used.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | tc |
Values | 0 or 1 (as bool; enabled or disabled; |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?tc=1 |
_______________________________________________________________
3.4.2 Preset
This parameter selects the transcoder preset for the current replay session.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | preset |
Values | 1 … 8 (selects one of the 8 transcoder |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?preset=3 |
3.4.3 Bitrate
This parameter sets the bitrate that is used by the transcoder for the current replay session.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | kbps |
Values | number (sets the bitrate in kbps) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?kbps=500 |
3.4.4 Frame skip
This parameter sets the skip rate that is used by the transcoder for the current replay session. A skip ratio of 1 means that no frame is skipped and the transcoded video stream uses the same frame rate as the original stream. A skip rate of 3 means that every 3rd frame is transcoded; hence the resulting frame rate is only 1/3rd of the original frame rate.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | skip |
Values | number (e.g. 1 = encode every 1st |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?skip=3 |
3.4.5 Video format
This parameter sets the video format of the transcoded video stream.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | fmt |
Values | 0 = do not change the video format (default) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?fmt=3 |
_______________________________________________________________
3.4.6 GOP size
This parameter controls the group of picture (GOP) size by setting the frame distance for sending intra frames in the transcoded video stream.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | ifrmdist |
Values | number (distance of consecutive intra frames; default = 60) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?ifrmdist=30 |
3.4.7 Timestamping
This parameter enables display stamping of the timestamp of the recorded data. That feature only works if Bosch SEI information or the ONVIF header extension is available in the recorded transcoder input.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | timestamp |
Values | 0 or 1 (as bool; enabled or disabled; |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/?timestamp=1 |
3.4.8 ROI horizontal position
This parameter controls the horizontal center of gravity of a region of interest (ROI) stream being requested from the transcoder. The coordinate system is normalized in a value range from 0 to 0x8000.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | roihpos |
Values | 0 … 0x8000 (in a normalized coordinate system; horizontal 0 is located on the left side of the video image; default = 0x4000 which represents the horizontal center of the image) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.1.100/ |
3.4.9 ROI vertical position
This parameter controls the vertical center of gravity of
a region of interest (ROI) stream being requested from
the transcoder. The coordinate system is normalized in a
value range from 0 to 0x8000.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | roivpos |
Values | 0 … 0x8000 (in a normalized coordinate system; vertical 0 is located on the bottom of the video image; default = 0x4000 which represents the vertical center of the image) |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/ |
3.4.10 ROI size
This parameter controls the relative size of a region of interest stream being requested from the transcoder. The size is given in relative values in a value range from 0 to 0x8000, where a value of 0 means ‘no region of interest’.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | roisize |
Values | 0 … 0x8000 (as relative size; default = 0 which means no ROI, |
Example | RTSP://160.10.0.1/ |
_______________________________________________________________
3.4.11 RTSP input source
This parameter enables the RTSP client of the transcoder, which is requesting the specified URL as the transcoder’s input.
Parameter and values | |
|---|---|
Parameter | url |
Values | RTSP URL to connect the transcoder’s RTSP client to the source (http escaped string) |
Example | Connection to the following url: |
3.4.12 Advanced example
Let’s assume an RTSP/RTP video source that is accessible via:
rtsp://user:u@160.10.0.200
should be transcoded on the transcoder device
160.10.1.100
with the following transcoder output parameters:
video resolution: 4CIF
video bit rate: 500 kbps
connection: TCP tunneled
The complete RTSP request that needs to be send to the
encoder would look like:
RTSP://160.10.1.100/rtsp_tunnel
?tc=1&fmt=3&kbps=500&fmt=3
&url=rtsp%3A%2F%2Fuser%3Au%40160.10.0.200
4 Technical Details
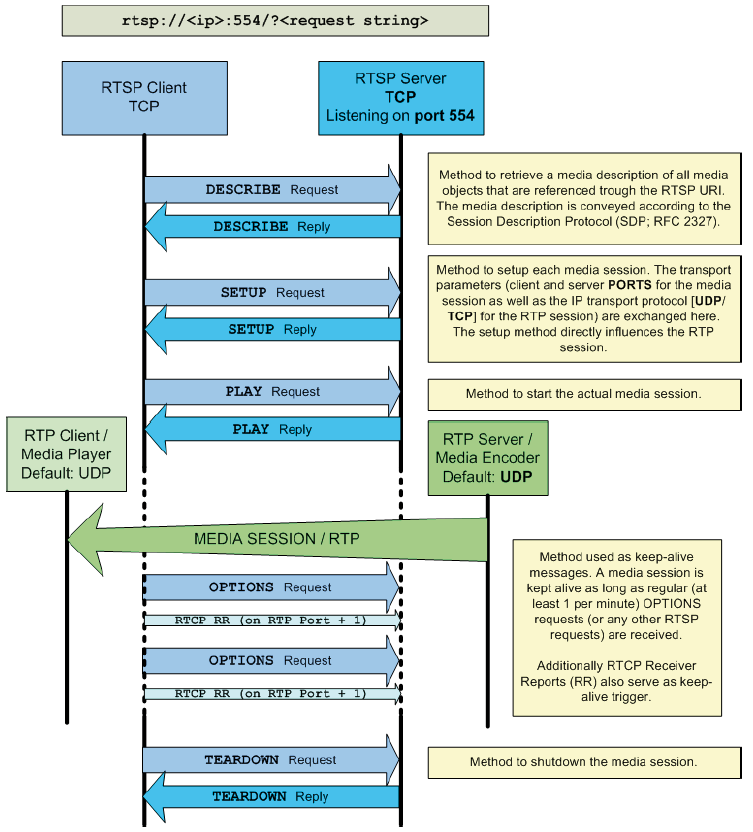
4.1 RTSP/RTP setup modes
According to the relevant RFC 2326 (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2326.txt) the Real Time Streaming Protocol, or RTSP is:
»… an application-level protocol for control over the delivery of data with real-time properties. RTSP provides an extensible framework to enable controlled, on-demand delivery of real-time data, such as audio and video.
Sources of data can include both live data feeds and stored clips. This protocol is intended to control multiple data delivery sessions, provide a means for choosing delivery channels such as UDP, multicast UDP and TCP, and
provide a means for choosing delivery mechanisms based upon RTP (RFC 1889).«
That means that the protocol specified various ways of setting up media connections over UDP or TCP media channels with a great flexibility but in turn also with some complexity. The following section is supposed to remove most of the complexity since it describes the relevant scenarios and features that are needed and taken into account when a media-client is interfacing with the Bosch BVIP RTSP server.
The RTSP session is referred to as the control session and uses TCP as transport protocol, whereas the RTP (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3550.txt) session is referred to as media session and by default uses UDP.
_______________________________________________________________
The typical RTSP server port is 554 and the media ports are negotiated during the session setup process. In a standard setup a media session uses 2 ports. The port-pair starts with an even port for the media session and is followed by an odd port for the RTCP (RTP Control Protocol: used for connection quality reporting and synchronization between different media sessions) information. That means that media ports are dynamically allocated and used but only one control port (RTSP port) is acquired.
In addition to the 'regular' session setup with the RTSP/TCP connection and the RTP/UDP connection RTSP also offers the possibility to fully use TCP when
needed (mostly when the network topology doesn't allow for UDP streaming). Setting the media session to use TCP instead of UDP is accomplished by changing the 'transport' parameter during the session setup. This is a feature that needs to be requested by the client and therefore (see following section 4.3) it needs to be enabled in the media-client. Such a setup is referred to as
»RTP over RTSP« or »Interleaved RTSP« mode.
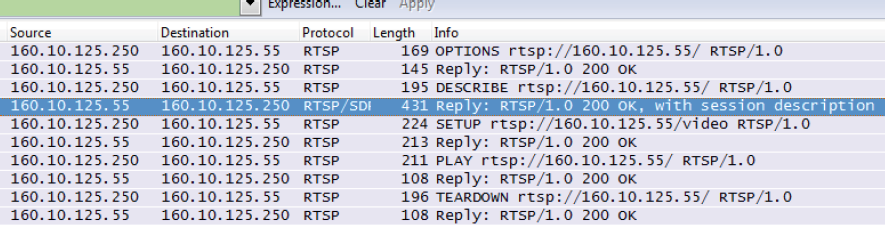
Typical use cases and control flow messages are depicted in the following charts. For a better understanding some of the charts are extended with some »Wireshark« screenshots that show a 'real-world' communication flow.
4.1.1 RTP/UDP setup
A typical trace in »Wireshark« looks like:
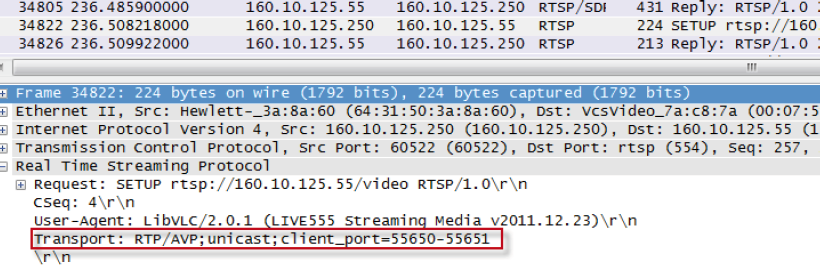
The requested media transport configuration can be identified in the SETUP request that is sent from the client to the server:
4.1.2 RTP/TCP setup
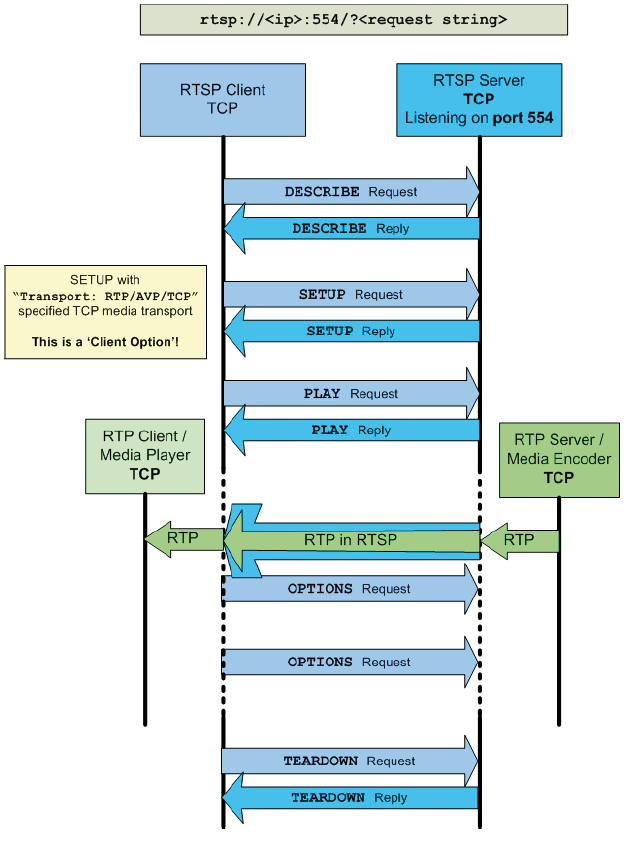
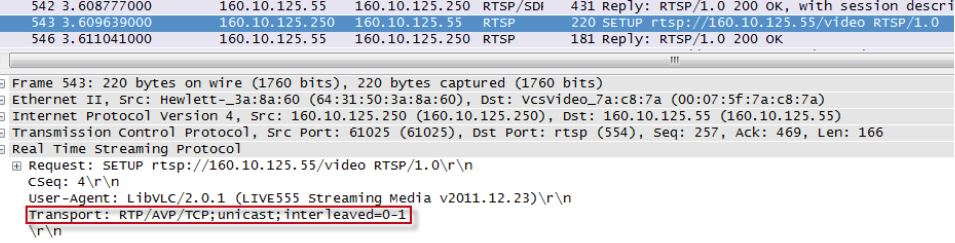
The according RTSP SETUP section to enable a TCP media connection looks like depicted below:
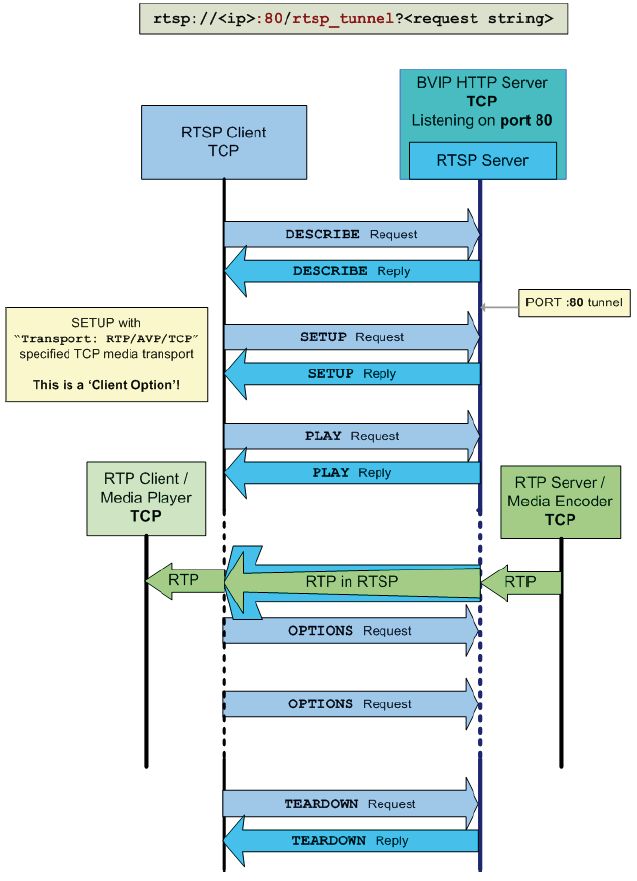
4.1.3 RTP/UDP tunneling setup
4.1.4 RTP multicast setup
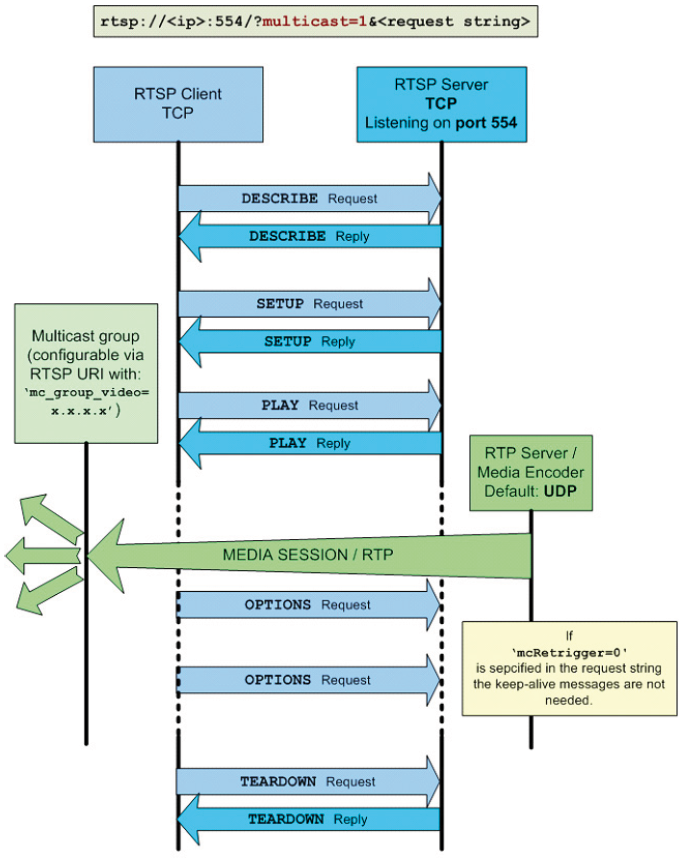
A typical RTSP request for a multicast connection with a multicast group (225.5.5.5) and a multicast port (6666) that was specified by the client is shown in the DESCRIBE request example below:
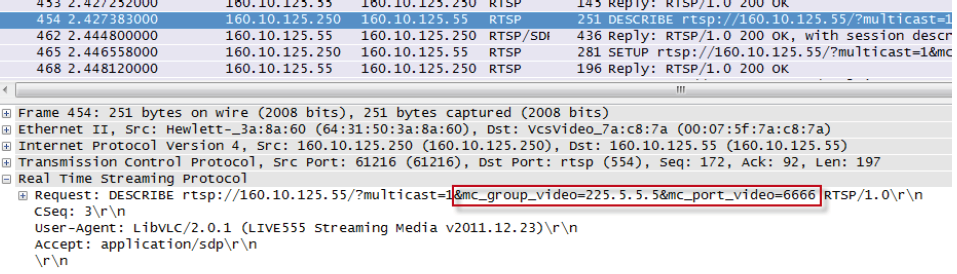
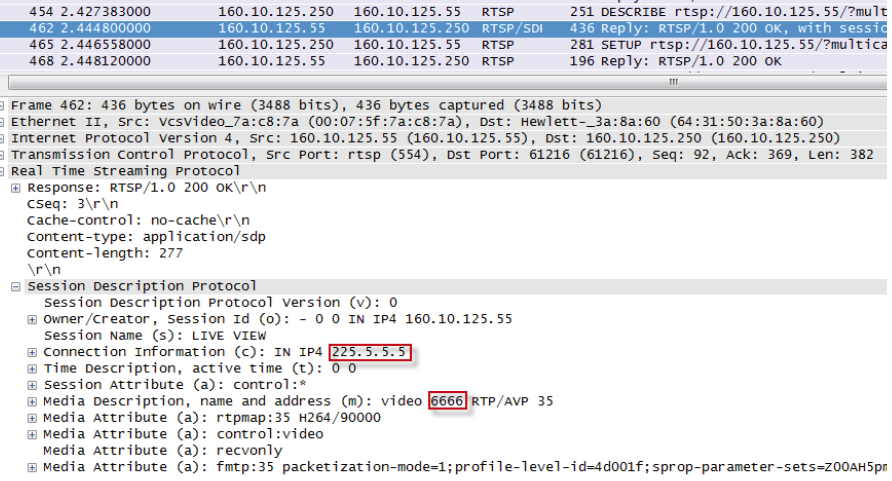
The RTSP server replies with a description of the session that is currently being set-up. The session description protocol (SDP) is used for this purpose and amongst
other necessary information the session's destination address and media ports are conveyed in the SDP string:
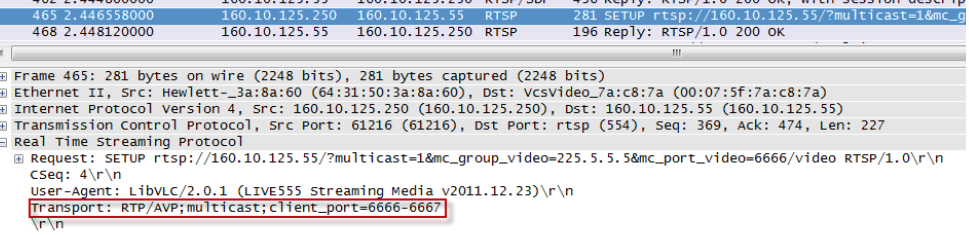
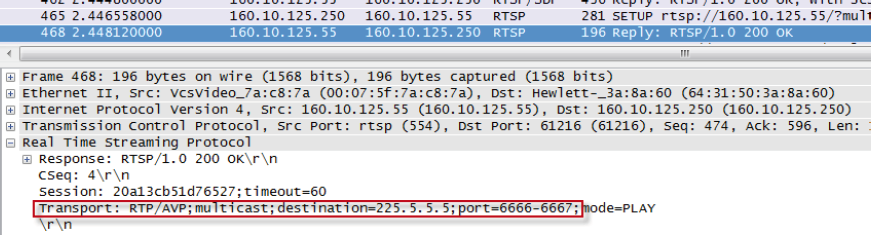
These session parameters are used in the SETUP request by the client and confirmed in the SETUP reply from the server:
4.2 RTP keep-alive/timeout
To avoid 'loose' media sessions a default timeout of 60 seconds is used in the RTSP server, which means that a media session is closed after 60 seconds without an indication (keep-alive message) of a client still listening to the session.
In unicast scenarios RTCP Receiver Reports (RR) or any RTSP command serves as keep-alive message, whereas in multicast sessions only the RTSP commands are applicable to keep a session up and running.
Any RTSP command from a client is interpreted as a 'sign of live' at server side but the usual command is the RTSP OPTIONS command since it does not interfere with active media sessions.
4.3 Setting up VLC for RTP/TCP tunneling
In order to use TCP tunneling some settings have to be checked in VLC.
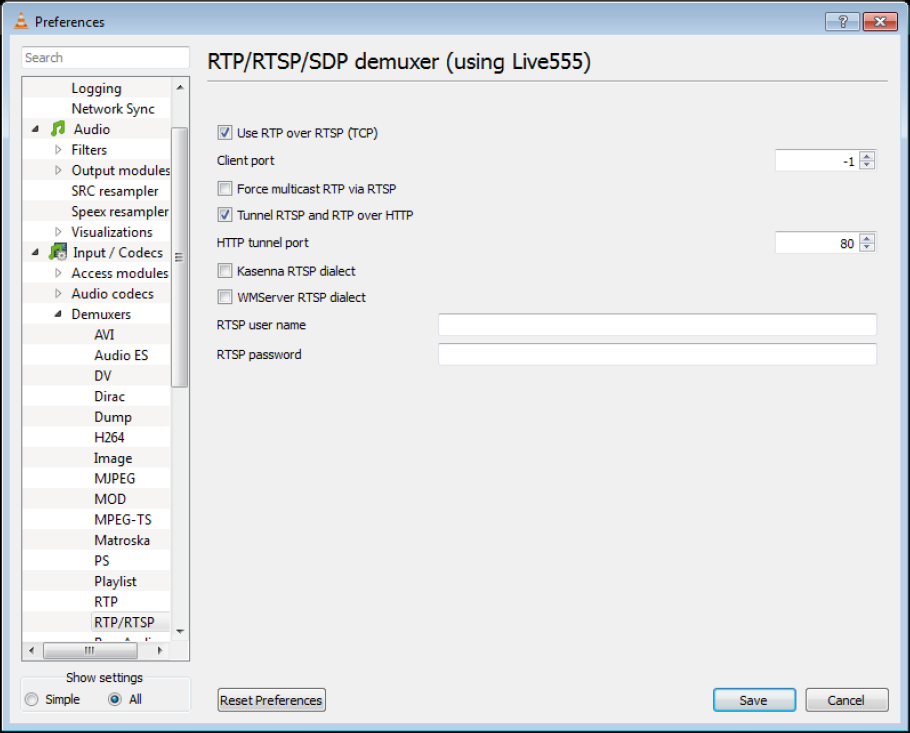
– Start the VLC.
– Choose Preferences from the Tools menu. The Preferences window opens.
– Switch the radio button at the bottom left side from Simple to All in order to show all settings.
– In the Input/Codecs section click on Demuxers.
– Click on RTP/RTSP.
– Check the box Use RTP over RTSP (TCP). This option sets the media session to be TCP; this is accomplished by multiplexing the RTP data into RTSP packets)
– Check the box Tunnel RTSP and RTP over HTTP. This option is the option to switch from the default RTSP port to a tunnel port; by default this is port 80.
– Click on Save to save the new settings and to close the window.
4.4 RTP replay timestamp, NTP time mapping
In order to allow clients to report a stable and accurate timestamp for each frame played back regardless of the direction of playback, it is necessary to associate an absolute timestamp with each packet, or each group of packets with the same RTP timestamp (e.g. a videoframe).
This is achieved using an RTP header extension containing an NTP timestamp and some additional information also useful for replay.
The replay mechanism uses the extension ID 0xABAC (= 43948) for the replay extension.
The screenshot shows a captured RTP replay packet which uses the referred RTP header extension.
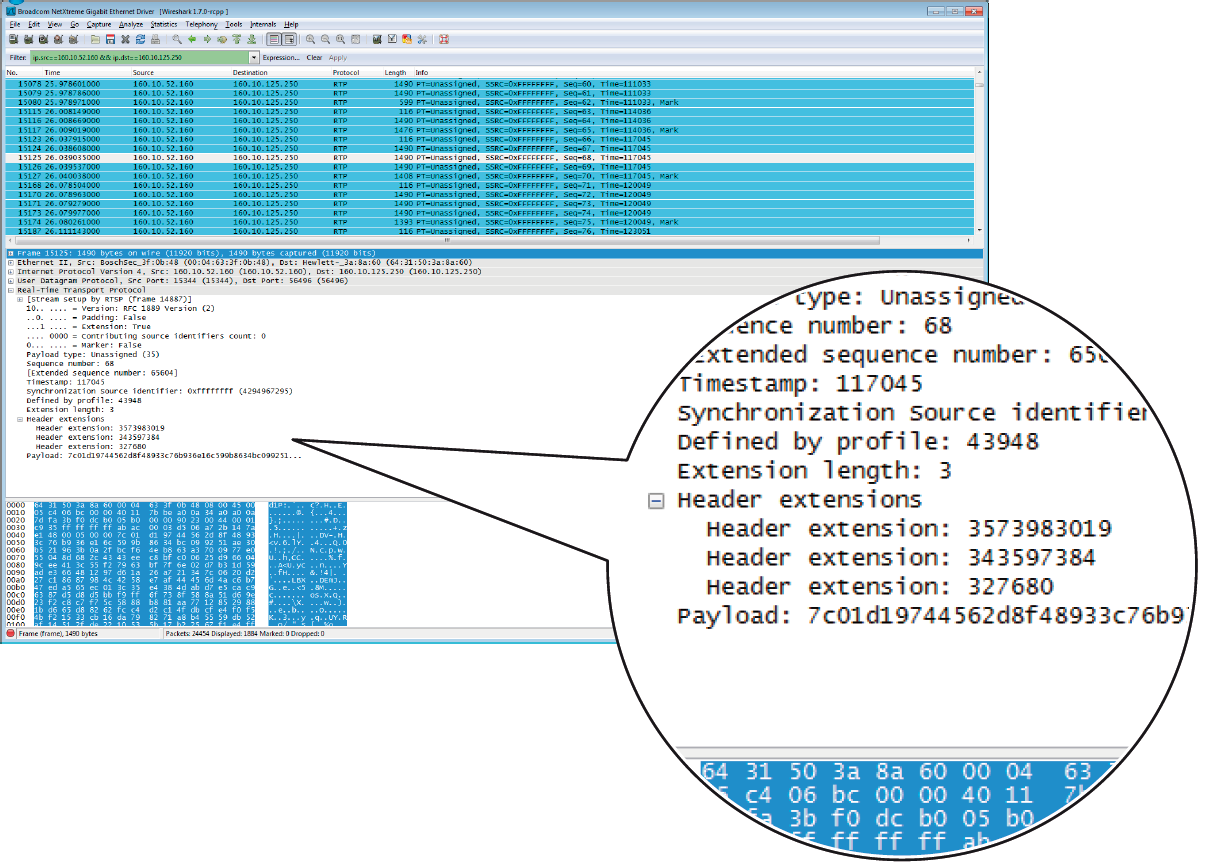
Defined by profile:
43948 = 0xABAC
Header extension:
3573983019 = NTP time: seconds from Jan 1st, 1900
343597384 = NTP time: fraction of seconds
In this example the time is 3573983019.343597384 seconds since Jan 1st, 1900 = April 3rd, 2013 @ 13:03:39 (343597384 / 2 ^ 32) UTC
